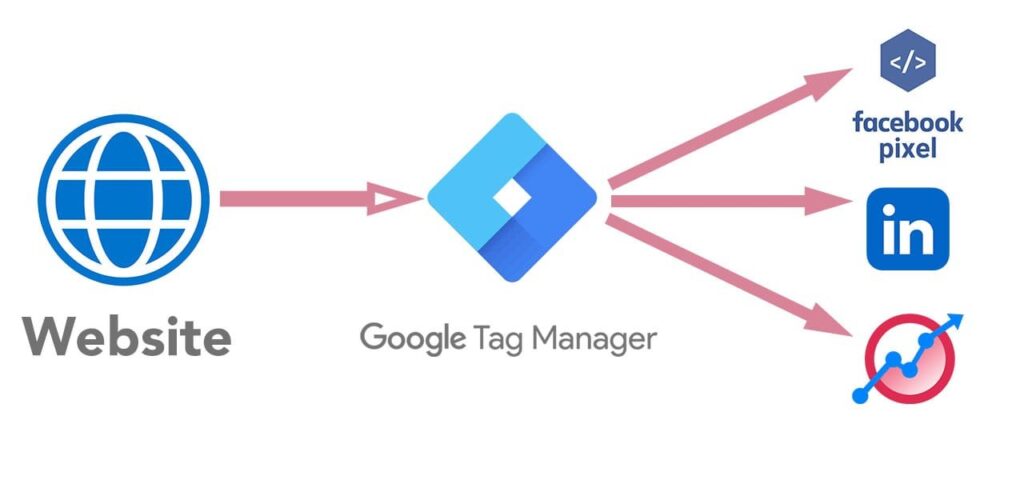
Have you ever wondered how businesses track their website visitor’s behaviour? Or how they optimise their advertising campaigns for better results? The answer is Google Tag Manager (GTM).
With Google Tag Manager, marketers and website owners can easily manage their tags and collect relevant data to gain insights into their website performance. In this article, we’ll dive into what exactly Google Tag Manager is and how it works to make your life easier. So, let’s get started!
1. Introduction to Google Tag Manager
Google Tag Manager is a powerful tool that allows users to manage their website’s tags effectively. A tag is a piece of code that sends data to analytics tools like Analyzati. GTM simplifies and streamlines this process by providing a user interface for creating, monitoring, and customizing tags without writing new code each time.
With GTM, users can easily add and update tags on their website for free, without needing to involve their IT department. This gives marketers greater flexibility and control over their tracking implementation, ultimately leading to better performance and ROI.
2. Benefits of using Google Tag Manager
After understanding what Google Tag Manager is and its importance in website analytics, it is necessary to know its benefits. One of the biggest advantages of Google Tag Manager is its elimination of the need for hard coding tags.
This enables website owners to implement advanced analytics tracking easily. Another advantage of Google Tag Manager is its ability to control all tags in one place, providing a simple and cost-effective solution for managing tags and code snippets. It can also track link clicks, automatically scan all tracking scripts and detect malware, and help websites load faster by minimizing the number of tags used. Overall, using Google Tag Manager can significantly improve website performance and facilitate analytics tracking.
3. How Google Tag Manager works
Google Tag Manager simplifies the process of adding tracking codes and pixels to a website by allowing marketers and developers to manage them through one platform. Through this tool, users can set up various tags, including GA tracking, conversion pixels, and remarketing codes, without needing to access the site’s back end.
Google Tag Manager works by placing a container code on a website and then creating tags, triggers, and variables within the Tag Manager platform. Tags act as tracking codes for events, such as button clicks, video views or form submissions, among others. Triggers define when tags are activated, while Variables are custom parameters that can be used to configure tags in a more personalized way. Overall, Google Tag Manager saves time, eliminates the need for developer support, and allows marketers to focus on the more strategic aspects of their campaigns.
4. Setting up Google Tag Manager
The first step is to install the tag on every page of your website using the instructions provided. This will allow you to start tracking data on your website immediately. It’s important to note that the first code block is best placed immediately after the web page’s opening. Once the tag is installed, you can customize it further by creating custom HTML tags and triggers in Tag Manager.
These tags and triggers allow you to send specific data to systems like Facebook, Analyzati, etc., giving you valuable insight into your website’s performance. Additionally, you can integrate Google Tag Manager with other tools to further enhance your tracking capabilities.
It’s important to avoid common mistakes in Tag Manager, such as duplicating tags and not testing tags before publishing. By following these steps and using advanced features of Google Tag Manager, you can effectively track your website’s performance and make data-driven decisions to improve it.
5. Customizing tags with Google Tag Manager
Customizing tags is one of the many advantages of using Google Tag Manager. With this feature, you can modify the snippets of JavaScript that are inserted into your website to suit your specific tracking needs. For example, you can add tags to track the performance of specific pages, measure the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns, or even analyze user behavior.
To customize tags in Google Tag Manager, you need to create a new Custom HTML tag and add your own code or modify existing tags to suit your specific requirements.
With Google Tag Manager’s intuitive interface and comprehensive debugging solutions, customizing tags has never been easier. By optimizing your tags, you can gain deeper insights into how your website performs and make better-informed decisions to improve your online presence.
6. Creating triggers and variables in Google Tag Manager
Creating triggers and variables is one of the most important tasks in Google Tag Manager. Triggers define the conditions under which tags should fire, such as clicks or pageviews. Variables, on the other hand, are used to store data that can be passed along to tags and triggers.
By using custom variables, website owners can make sure that all the data they need for analytics and other tracking is available in GTM. When building tags, it is important to understand how the triggers and variables work, so that the tags are firing correctly.
Mistakes in this area are common and can lead to erroneous data being sent to analytics tools. Thus, website owners are advised to take the time to learn how to create triggers and variables in Google Tag Manager to ensure that their tracking implementation is accurate and comprehensive.
7. Common mistakes to avoid in Google Tag Manager
One mistake to avoid is incorrect implementation of the GTM snippet. It is important to use other debugging tools, check real-time reports, and completely remove old implementations to avoid duplicate scripts running.
Another mistake is forgetting to audit GA or testing with the wrong URL. Additionally, not publishing the GTM container can also cause issues. To customize tags effectively, one must also create triggers and variables. Outdated tracking code also hinders tracking performance. By integrating Google Tag Manager with other tools, tracking performance can be optimized.
Finally, understanding advanced features of Google Tag Manager can greatly improve its usefulness. By avoiding these common mistakes, businesses can fully utilize the potential of Google Tag Manager for their website tracking needs.
8. Integrating Google Tag Manager with other tools
Integrating Google Tag Manager with other tools can help businesses gain even more insight into their website performance. With Tag Manager’s easy integration capabilities, it can work seamlessly with Analyzati or other third-party tools to further optimize and track user behavior.
By integrating Google Tag Manager with other tools such as heat mapping software, businesses can gain a better understanding of where users are clicking or scrolling, and adjust their website accordingly.
It’s also possible to integrate Tag Manager with CRM or marketing automation tools to better analyze customer interactions and personalize marketing efforts. By utilizing these integrations, businesses can enhance their overall marketing strategy and improve their website’s performance.
9. Tracking performance with Google Tag Manager
In order to effectively measure the success of your digital marketing efforts, tracking performance is essential. Google Tag Manager makes it easy to track and analyze data from all of your tags in one central location.
With Google Tag Manager, you can easily set up tracking for key metrics such as website traffic, page visits, and conversion rates. By customizing your tags using triggers and variables, you can track specific user actions and gain valuable insights into the behavior of your website visitors.
Integrating Google Tag Manager with other tools such as Analyzati and Google Ads allows you to track performance across multiple channels and make data-driven decisions to improve your marketing strategies.
With the advanced features of Google Tag Manager, you can even set up complex events and triggering rules for even more accurate tracking. In short, tracking performance with Google Tag Manager is an essential component for any successful digital marketing campaign.
10. Advanced features of Google Tag Manager.
Once you’ve become comfortable with the basics of Google Tag Manager, you might want to dive into its more advanced features.
Here are some of the key features that users can leverage: version control, debugging and previewing, custom templates, and JavaScript variables.
With version control, you can deploy different versions of your container to different environments, like staging and live sites. Debugging and previewing helps ensure that your tags and triggers work as expected before publishing.
Custom templates offer a way to reuse and share tag configurations across multiple accounts or containers. Lastly, with JavaScript variables, you can create custom variables that aren’t natively supported by Google Tag Manager.
By taking advantage of these advanced features, you can streamline your tracking and analytics processes even further.
11. Google Tag Manager uses cookies ?
As you may know, Analyzati is a privacy-focused-fiendly analytics tool, what means that we don’t use cookies and therefore you don’t need to use a cookie consent in your website.
Google Tag Manager does not collect, store or share any PII about visitors to its users. Neither does it use tracking technologies like cookies.
12. How to integrate Analyzati analytics using Google Tag Manager?
We have created a detailed help with a few simple steps. Jus follow the guide here and start tracking your website visitors and behaviour.
Conclusion
Google Tag Manager can simplify your life and can provide you more control with your website integrations. Is recommended that you test before using Google Tag Manager to avoid causing data lost or unexpected behaviour in your website.